When it comes to neurological health, the eyes play a pivotal role in providing information that can aid in the understanding and diagnosis of various underlying conditions. Pupil assessment or measurement also referred to as measuring the size of our pupils is tools used in neurology. This detailed guide delves into methods for measuring pupil diameter
The Importance of Assessing Pupils in Neurology
Evaluating pupils is much more than a medical procedure. It serves as a pathway to unravel the enigmas surrounding the human nervous system.
Here’s why it holds significance:
Early Detection of Abnormalities: Measuring pupil diameter can act as a warning system for neurological irregularities. Anisocoria, which is basically differences in pupil size can indicate underlying issues like damage to cranial nerves, brain injuries, or even the presence of tumors. By measuring and comparing pupils, healthcare professionals can promptly address these abnormalities.
Monitoring Neurological Conditions: Regular evaluation of pupils greatly benefits patients with existing neurological conditions. Changes in pupil size can serve as an indicator of the progression of symptoms or the emergence of complications. For example, if intracranial pressure (ICP) is elevated or if there is herniation, fixed and dilated pupils may signify an emergency that requires intervention.
Mastering the Techniques of Pupil Size Measurement
There is no one-size-fits-all technique when it comes to neurology and neurological evaluation. There are various methods and tests that medical professional uses to get the precise result of pupillary evaluation. Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages. Let’s talk about a how to measure pupil size:
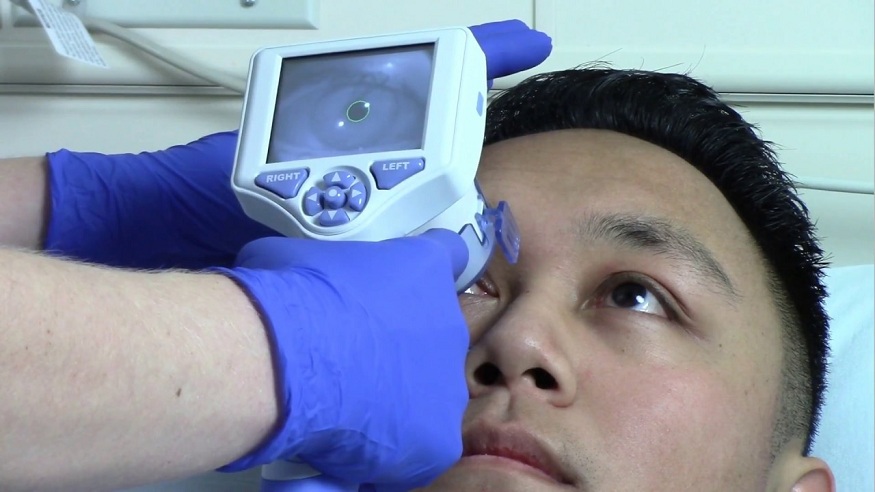
Direct Pupil measurement: This specific method uses a pupillometer to unswervingly measure pupil diameter in millimeters. This method is usually employed in specialized neurology settings or research.
Swinging Flashlight Test: This is one of the most common techniques, and involves alternating a source of light between two pupils to evaluate the comparative or relative pupillary constriction in each eye. This technique is highly used for detecting anisocoria.
Pupillary Response to Light: This is one of the fundamental methods where a light source is generally used to detect how pupils are reacting to the light intensity changes. Usually, pupils constrict in response to bright light and dilate in dim light. If the pupils are not reacting as per the set rules then there is a high chance of underlying neurological issues.
Dynamic Pupillometry: This technique involves real-time and continuous monitoring of pupillary size measurement. This method is very useful in critical care settings identify a subtle change that might be a symptom of underlying neurological problems.
Video Pupillometry: Video pupillometry records and scrutinizes the response of pupils to the intensity of light and provides quantitative data. These data are useful in continuous patient monitoring and neurological research.
Data: The Backbone of Pupil diameter measurement
Data is the heart and backbone of pupil assessment, and pupil measurement. It is important to note that taking baseline measurements helps to identify even the slightest change among patients. The need for regular, correct gathering and analysis of data concerning the neurology of a patient lies in the essence by definition. Such gathering concerns chronic neurological disorders as well as persons at immediate risk of stroke.
A pupillometry study among TBIs showed that it is related to injury and severity. A pupillary measurement was found to be a valid predictor of the level of head injury and consequently, the degree of the neurological disorder, providing an individual approach to treatment.
Wrapping Up
Pupil assessment is a standard practice in neuroscience that is not intrusive and provides vital data on complex matters associated with nerves’ functioning, diagnoses of pathologies, and control procedures for patients whose life depends on the nervous system. Each of these techniques gives healthcare providers a glimpse into a patient’s neurological state such as the direct measurement, swinging flashlight test, pupillary response evaluation, dynamic pupillometry, and video pupillometry.
Clinicians would be able to understand the neurofunctional status of their patients by carefully collecting and analyzing the information concerning the pupils’ functions. Additionally, tracking changes in the condition through time will also enable them to develop a good plan of care or intervention. The size of the pupil in neurology is more than just a measure—it’s an important medical device employed by neurologists. It’s like seeing things versus making them out.